-
"This page will maintain list of AI related libraries for the Ruby programming language." Some interesting stuff here, although it's all in varying degrees of maturity…
-
"What data can we wring out of the rural environment that might prove of use to it’s residents and visitors? What embedded processes should have APIs opened up to the wider community?" Lovely lovely lovely design of little bits of Ruricomp and what they might look like from the lovely lovely Paul Pod (who was in the studio a week or two ago, and a joy to work with and around). The twitterbots are especially good.
-
"We’ve been working with the fine folks at Flickr (thanks Aaron!) to add Noticings to their third party machine tag services. What on earth does that mean? Basically, a badge on the sidebar of your Flickr photos linking to Noticings…" Ding! Rather excited about this. Lots more to come (especially from my half of the deal) on Noticings soon, but this bit is super-exciting.
-
Freddie25 plays the Wind Waker theme, on a selection of instruments, as a Christmas treat for you. It's delightful, and the bit when the nine-part vocals come in is lovely. Proper good, this.
-
"..some tweets were destined for fail." – or, at least, not for public consumption. Oh dear.
Twit 4 Dead: more silly nonsense with Twitter bots.
29 December 2008
As a little post-Christmas present, I thought I’d share a little code toy I’ve been working on recently.
You might know that I’m a fan of Twitter as a messaging bus, and I’ve already built some entertainingly daft bots in my time with it. Recently, I decided to flex my programming skills a bit and build not one but four bots. And, more specifically: four bots that talk to each other.
Enter @louis_l4d, @zoey_l4d, @bill_l4d and @francis_l4d. You might notice that they’re named for the characters in Left 4 Dead.
This is not a coincidence.
One of the most wonderful things in that game (which I’ve already commented on the brilliance of) is the banter between the four player characters. There’s so much dense, specific scripting, and enough dialogue so that it rarely repeats. I thought it would be interesting to see if you could simulate the four players’ dialogue over Twitter, sharing some state between the bots, but also finding a way to make them communicate a little with each other.
Well, a bit later, I worked out how, and this is the result:

You get the picture. They run a scenario, they bump into boss zombies, they find stuff, they get hurt (and help each other), they get scared (and reassure each other). At the moment, there are some dialogue overlaps; my main work at the moment is adding more unique dialogue for each bot. Bill is sounding pretty good, but the rest of them need work. It takes about 2-3 hours for them to run a scenario, and it’s usually fun to watch. (And, as you can see, it makes sense to follow all four of them).
So how does it work?
It turned out that rather than trying to build any real AI, it was much more fun just to simulate intelligence. The bots are state machines; they have a variety of states, which they transition in or out of dependent on factors, and suitable dialogue for each state.
I wrote the bots in Ruby. There are two main components to the twit4dead code: the Actor class and the Stage class. The Stage is a singleton; it’s where the state of the world is determined, and global variables tracked. It’s also where all the probabilities are run from. The Actor class is what each of the bots are, and it’s based on the Alter Ego state-machine library for Ruby. We have a lot of states, rules for transition, a selection of methods to handle being helped or talked to by friends, and a method to choose a random piece of dialogue appropriate to the current state.
All the bots are instantiated from a YAML file. For each bot, I store its Twitter username and password, and a nested tree of dialogue for each state. This means it’s really easy to add new states and maintain the dialogue for each bot. It’s also easy to add new bots – you just create a top-level entry in the YAML file.
Originally, I thought about the bots broadcasting and listening over Twitter, but the API calls were just going to get out of hand, and it turned out that Twitter didn’t like being bombarded with messages and would drop a few over time. So I separated out writing the script and broadcasting it. A small utility generates a script file; each line of this file consists of three delimited fields for username, password, and message to send to Twitter. Then, another program – which I currently run on a screened shell – reads that file and broadcasts one line of it every minute until it’s done.
And that’s it. I have to run it by hand for now, which is fine – it’s more something I fire up every now and then, rather than something you want to permanently run. I originally was going to keep track of loads of statistics – health, zombies in play, etc – but found a cruder set of rules worked much better. Every time they’re in combat, there’s a slim chance somebody gets hurt; every time somebody’s hurt, a friend will rush to save them. That sort of thing. Simulated Intelligence, then, rather than Artificial Intelligence.
Alter Ego turned out to be a lovely library; dead simple to use, and as a result the bots are really nicely modelled (or, at least, I’m very happy with how they’re modelled). The notion of a Stage with Actors, rather than a Game with Players, feels about right, and the modularity of it all is pretty nifty. It still requires a little refactoring, but the architecture is solid, and I’m proud of that.
I think my favourite aspect of it, though, is that at times, watching the bots play together is a little like magic. The first time I saw them talk to each other, cover each other whilst reloading, help each other up after a Boomer attacked, I felt a little (only a little, mind) like a proud father. They’re dumb as a sack of hammers, but they look convincing, and that was the real goal. It’s fun to watch them fight the horde amidst all my other friends on Twitter.
Nonsense, then, but a fun learning exercise about state machines, object orientation, and simulating conversations. State machines are a ton of fun and if you’ve not seriously played with them, I thoroughly recommend it.
Do follow the four of them, if you fancy; I’ll make sure I run them with reasonable regularity, and I’ll be fixing the dialogue over time. After all, I want to keep Francis happy.
-
"As the population of the system grows, everyone's personal horizons begin to shrink. With enough people, eventually you're talking to the people right in your neighborhood. To get a message to someone across the country, you might lie about your location, or ask that it be passed on, Milgram-style." Filtering by proximity in a restrictive – but potentially more useful – manner. Interesting.
-
"This is the challenge, it seems to me: it's to do with the tools of design– rules and states– what other media do with images and sound: reveal the world as seen through different eyes, with lapidary clarity and moral courage. And this means moving beyond merely empowering and entertaining the player."
-
"Everything breaks, so what happens when we wire the world on the sort of massive scale being proposed and every day is more irritating than the next? Probably what will happen is that people will just walk away from the entire project damning it first with market insignificance and if that doesn't work then rendering it meaningless with government regulation. It's worth at least talking about." Aaron is awesome.
Twitter: a messaging bus for telescopes (and almost anything else you’d like to overhear)
22 May 2007
One of the things that’s been making me happiest recently has been the fact that Jodrell Bank’s telescopes have been Twittering. These big machines, peering into the cosmos, chattering to themselves about where they’re currently pointed – and that chatter is overheard and reproduced on the web. Obligatory screengrab, in case Twitter is down:
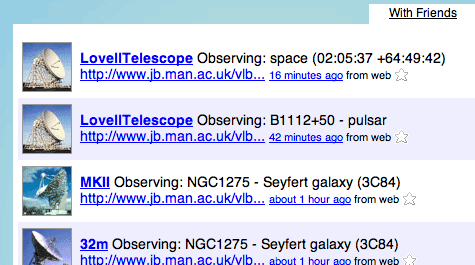
It’s cute, and adds to the growing number of non-humans burbling away on Twitter. As I thought about this, it became clear that Twitter isn’t just “the status message turned into communication” (as I usually describe it), but a human-readable messaging bus.
Continue reading this post…
Availabot!
25 June 2006
So, now that Jack‘s show is happening, S&W have finally decloaked Availabot.
Wow. Suddenly lots of cryptic conversations with Matt over the past few months make sense – mass production, Chinese toy factories, the hell of USB serial communications.
It’s a lovely thing. I really like the emphasis on the individuality – rapid fabrication of appearance, username hard-coded into hardware – one physical thing represents one digital thing, and it’s obvious and understandable without the need for a Thinglink idea or a product code. Matt Jones’ Availabot looks like Matt Jones. When I hand you the red-headed one with a quiff, you know it’s mine; plug it into your computer and that’ll confirm it.
Also, it harks back to the peripheral vision idea of Glancing, I guess; I really like this quotation on the page:
Rather than showing up on your screen, it shows availability as a physical object in the world. That means that you can move the puppet out of view when you don’t want to be distracted, watch out for it when you’re working on other tasks, and have a background awareness of your friends from the corner of your eye.
Hiding things by hiding them on your desk, not your “desktop”. Paper bags, stacks of books, not command-H. We procrastinate (or indicate busy-ness) physically, after all. Made me grin.
Anyhow: awesome concept, probably complex in execution, but very elegant nontheless. I hope it goes somewhere!